
Psychology is the fascinating study of human behavior. It holds incredible potential for eCommerce seeking to boost their sales and thrive online.
By simply understanding the psychology behind consumer decision-making, ecommerce can unleash a powerful arsenal of techniques to drive conversions and cultivate customer loyalty.
This article delves into 14 proven psychological tricks for eCommerce sales and strategies.
From leveraging cognitive biases to mastering the art of persuasion, these tactics are designed to resonate with your target audience and empower them to make purchase decisions confidently.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on the most critical journey of growing an eCommerce.
1. Price anchoring
Price anchoring is a common psychological trick influencing people’s perception of a product’s value. It is a trick that can help you establish a base and a discounted price to showcase the offer customers are getting.
And we see examples of this trick all the time.
It presents the product as expensive at first and then discounts it.
Because customers know the base price, the lower price is always perceived as a good deal.
Williams Sonoma, a home furnishings retailer, is known for using a price anchoring trick. By listing original high prices next to discounted prices, Williams Sonoma makes the discounted prices seem more attractive.
Price anchoring can be a very effective way to increase sales.
However, it is essential to use this trick carefully. If you anchor people with a price that is too high—unreasonable pricing to keep it short—they might not even be willing to buy your product at any cost.
2. Scarcity principle
The scarcity principle is another common eCommerce psychological trick to influence purchasing decisions.
This trick works by showcasing a product’s scarcity and making it more desirable. This trick is used in various ways, so let’s go through them.
One way is to limit the availability of a product. A typical example of this is “limited edition” products.
While most brands can easily replicate the production of the product, they only sell/create a limited number of products. This exclusivity creates lower supply, high demand, and hence high pricing.
Another way to create a sense of scarcity is to make people feel like they are competing for a product.
We most commonly see it on Amazon. The eCommerce giant often uses the scarcity principle by displaying messages like “Only 3 items left in stock“. This surely creates a sense of urgency and encourages immediate purchases.
The scarcity principle is a very effective way to increase sales. But it’s essential to be aware that excessive use of this trick might immunize your customers of it over a long time.
3. High manufacture cost portrayal and presentation
High manufacturing cost portrayal is a psychological trick that can inflate the cost of products and increase the perceived value.
This trick works by making people think that a product is more expensive than it is. Prominent brands use ecommerce photo editing services to make their products look more expensive and luxurious.
This includes clean background, product alignment, color consistency, lint removal, spot removal, retouching, and more.
Next is the line is the branding and the story behind the brand. Tiffany & Co is a luxury jewelry brand that emphasizes the craftsmanship and high-quality materials used in their products.
Through marketing campaigns, high-quality presentation, and creating the perception of exclusivity, Tiffany & Co justify its luxury prices and present itself as a premium brand.
4. Fear of missing out (FOMO)
FOMO, or Fear of missing out, is among the most famous psychological phenomena—thanks to social media and Genz lingo.
FOMO is the Fear that one might miss out on something others have. This could be a trend, a product, an experience, and everything a social group is involved in.
This Fear can be compelling and lead people to buy products they don’t need.
There are a few different ways to create FOMO. One way is to make people feel like they are missing out on a trend.
Supreme is one of the most popular brands that use FOMO as their bait for sale. While the products range from Tees to crossbars and brick—Supreme follows a drop strategy.
They release limited products for a limited time, and once the products are sold out—they are never restocked.
This scarcity creates a rush. People who have it flaunt it widely on Social media and on the street.
This creates a viral effect where hence people in the target group feel like they are missing out. Hence the next drop is even more successful and viral.
5. Social validation
Social validation is a psychological phenomenon embedded within the human psyche. Being accepted by the tribe and valued by the tribe is highly valuable to each individual.
And this factor can be used to influence purchasing decisions of the customers. This trick makes people feel like they are making the right decision by buying what others already trust.
Reviews, recommendations, and user-generated content are some common social validation signals.
There are several ways to create social validation for an eCommerce brand. And the most common method is through positive reviews of your product.
Another way is to show people that other people are buying your product. Motivating customers to use your product and creating social media content can create social validation for your customers.
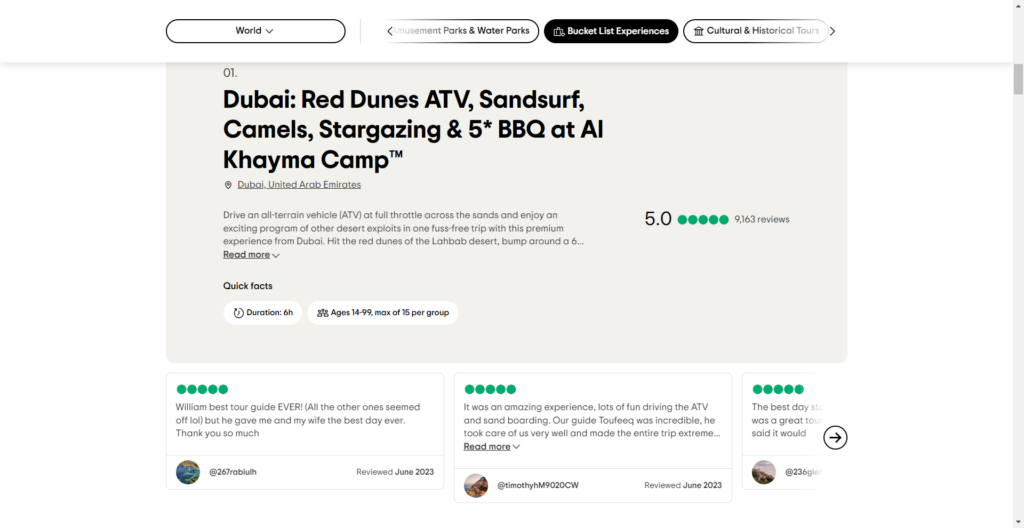
Travel website TripAdvisor uses social validation by prominently displaying user reviews and ratings for their travel experience, helping new potential customers make informed decisions. And this is based on the experiences of others.
6. Loss aversion
Unlike other eCommerce psychological tricks that tell a customer what to do, loss aversion influences what not to do or, more commonly, what a customer can avoid.
Loss aversion is a psychological bias that makes people more likely to avoid losses than achieve gains. A typical example of a Loss aversion trick in practice is using a Countdown timer or flash sales.
If someone is participating in a flash sale or an offer with a timer—they are aware of the risk—the risk of losing the opportunity to get a product at the best price.
And this has proven to be highly effective as well. SaleCycle shared that adding a countdown can increase the click-through rate by 30% and conversion by 200%.
7. Micropayments
Micropayments are the small payments that customers can make over a more extended time after buying a product. The most common term for the same is Buy Now Pay Later schemes.
These are like financial aids that allow customers to buy a product now and pay for the product in small installments in upcoming weeks.
Result? Increase in sales. Top fashion brands like ASOS, H&M, & Nike saw an average of 15% increase in their sales. Additionally, these modes of payment reduced cart abandonment by 30%.
And all this is due to the lower barrier and stakes on the line. Rather than making a $100 purchase, people can opt for a $25 weekly payment and quickly get the product.
Micropayments are effective because they make it easy for people to make small purchases. This is important because people are more likely to purchase if they don’t have to think about it too much.
8. Bundling
Bundling is an eCommerce and psychological marketing trick mainly used to increase sales and cart value. Here, rather than telling customers to buy more/different types of products together as a package.
Bundling is practical because it seems like you are getting a good deal. Firstly, giving a bulk discount is easier for eCommerce. Order handling becomes much easier, and all sales KPIs are positively impacted.
For customers, it gives them the best deal, helps them pick the best combination of products, and saves time on shipping costs.
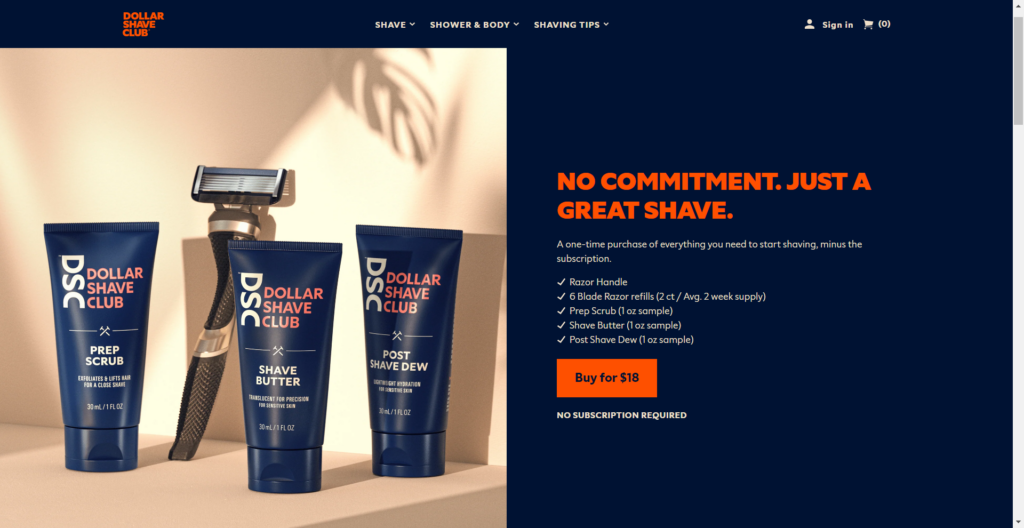
Dollar Shave Club uses one of the best examples of bundling psychological tricks.
It is a subscription service offering razors, shaving cream, and other shaving products. They have increased the average order value and kept customers subscribed for a more extended time.
On the other hand, customers receive their self-care package every month without friction to place an order each month.
9. Decoy effect
The Decoy effect is a gray psychological trick that must be used wisely. To use this strategy, eCommerce presents multiple options for the customers to choose from.
And while it might seem like a customer has multiple options, eCommerce puts a decoy that influences the customer’s buying decision.
Let’s understand this better with an example here. The Economist is a popular magazine that is available both online and offline. They experimented with three subscription options:
- $59 for Online only
- $125 for Print only
- $125 for Print & Online
Adding the second option of Print only is an excellent example of the decoy effect. Why would someone get only one when they can get both at the price of both online and offline subscriptions? Right?
Well, here’s something we must note. We have already neglected the first while discussing the best deal between the second and third options.
That’s how a decoy influences the buying decision. While many customers would go for the Print & Online option—because of the decoy—they might simply ignore the first one.
10. The Gruen Transfer
The Gruen Transfer is a psychological phenomenon in that transfers create a sense of excitement and urgency in shoppers. As you might know, the most common name of this phenomenon is the IKEA effect.
IKEA is a home furnishing store chain where people can buy disassembled, DIY furniture rather than ready-made furniture at the best price.
The Gruen transfer comes into play when customers build the furniture by themselves. They are more involved with the product and brand and are hooked on the experience.
This often reflects in word-of-mouth marketing and returning customers, which helps a brand grow.
11. Periodic Equivalent Pricing
Periodic Equivalent Pricing is a psychological pricing trick for eCommerce with the subscription. This trick suggests showcasing the cost per unit rather than telling customers about the total subscription price.
Unlike regular online retailing, subscription retail has to convince customers to sign up for a monthly payout. And while the overall value of the subscription might be the same, breaking it down to each unit makes it appear more accessible to a broader audience.
Let’s understand this with a suitable example of Blue Apron, a meal kit delivery service that delivers pre-portioned ingredients and recipes to customers’ doorsteps.
A customer can choose the number of servings and meals per week. Look at their product page to understand how Periodic Equivalent Pricing is used.
Instead of presenting the total price of the plan, Blue Apron tells us the cost per meal we are paying. It makes a convincing case for many and helps eCommerce boost its subscription rate.
12. Parasite placements
Just like the Decoy effect we discussed, Parasite placement is a psychological trick that relies on the placement of the product. But here’s a difference.
While using the Decoy effect, eCommerce puts up an offer that isn’t worth it since customers are getting the same value at a lower price.
In Parasite placement, on the other hand, eCommerce places its high-end products near affordable options.
This is to make their high-end product look like a better deal or premium set of products. Let’s take the example of Apple. The tech giant often positions its higher-priced products next to lower-priced alternatives in retail stores.
While for some brands, this might put them at a disadvantage, for Apple, it makes their products appear more premium and desirable by comparison.
13. Simple pricing strategy
A simple pricing strategy is a psychological trick at almost every retail store. Instead of pricing as a whole, eCommerce reduces the pricing just a little.
Ecommerce will price their products at $19.99 instead of $20. The change is tiny and might barely make a difference for a customer, but in terms of conversion, it draws attention.
Entrepreneur.com has shared pricing a product just a penny or two below the dollar can increase conversion by 21-34%.
For a penny less, this is a great bargain for any eCommerce.
14. Baader-Meinhof phenomenon
The Baader-Meinhof phenomenon, also known as the Frequency illusion, is a psychological phenomenon that can be used to increase sales. This phenomenon makes people think they see something more often than they are.
Brands like Nike effectively utilize the Frequency illusion by collaborating with athletes, celebrities, and influencers and launching limited-edition collections.
This creates a sense of ubiquity, making their products more noticeable and driving consumer interest.
Retailers can use this phenomenon to increase sales. One can use this phenomenon and create social media campaigns and specific product placements to gain desirable attention.
Conclusion
These are just a few of the many psychological tricks that can be used to increase ecommerce sales. By understanding these tricks, ecommerce businesses can use them to increase sales.
However, it is essential to use these tricks carefully. If you use these tricks too often, or if you use them in an unethical way, you could alienate your customers.
Testing different psychological tricks to see what works best for your business is also essential. What works for one business might not work for another company.
By understanding and using psychological tricks, ecommerce businesses can increase their sales and grow their businesses.
Featured image by Pixabay on Pexels
The post 14 Psychological Tricks To Grow Your Ecommerce Sales appeared first on noupe.